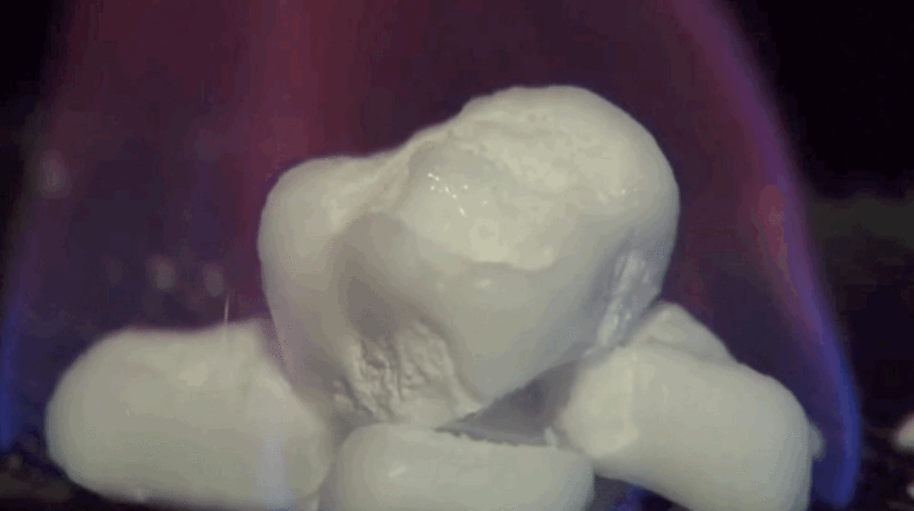
Methane hydrate is a type of icy natural gas that accumulates in the subsurface around the Earth’s continental margins. Because methane is a hydrocarbon, the icy hydrate deposits are an important part of the carbon cycle, accounting for billions of tons — up to 22% — of Earth’s organic carbon. The methane feeding this layer… Continue Reading Making Methane from Microbes: UTIG and UT Knoxville Hunt for Biological Source of Fiery Ice
UT Austin Studies Mysterious Substance that Could Transform the Future of Energy
In 2017, UT Austin geoscientists led the first U.S. university-based expedition to the Gulf of Mexico in search of methane hydrates. Today, they are at the forefront of research to understand this possible new energy source. A UT News exclusive by Tracy Zhang.
Pressure Coring Technology One Step Closer to Gulf of Mexico Hydrates Test
By Constantino Panagopulos It’s mid-March on the Texas prairie outside the city of Cameron. Peter Flemings, a professor at the Jackson School of Geosciences, watches the rig hands lower the prototype sensor into the well. The counter still reads 1,000 feet from bottom when the thick steel cable suddenly goes slack. Moments later a dull… Continue Reading Pressure Coring Technology One Step Closer to Gulf of Mexico Hydrates Test
Computer Model Solves Mystery of How Gas Bubbles Build Big Methane Hydrate Deposits
New research from The University of Texas at Austin has explained an important mystery about natural gas hydrate formations and, in doing so, advanced scientists’ understanding of how gas hydrates could contribute to climate change and energy security. The research used a computer model of gas bubbles flowing through hydrate deposits, a common phenomenon which… Continue Reading Computer Model Solves Mystery of How Gas Bubbles Build Big Methane Hydrate Deposits
Where Do Natural Gas Hydrates Come from and Why Should We Care?
A new generation of models, laboratory, and field studies is helping scientists answer important questions about the role of methane hydrates in the carbon cycle and as a possible energy source. Writing in Eos Editor’s Vox, Kehua You and Peter Flemings answer questions about why studying this mysterious substance is more important than ever.