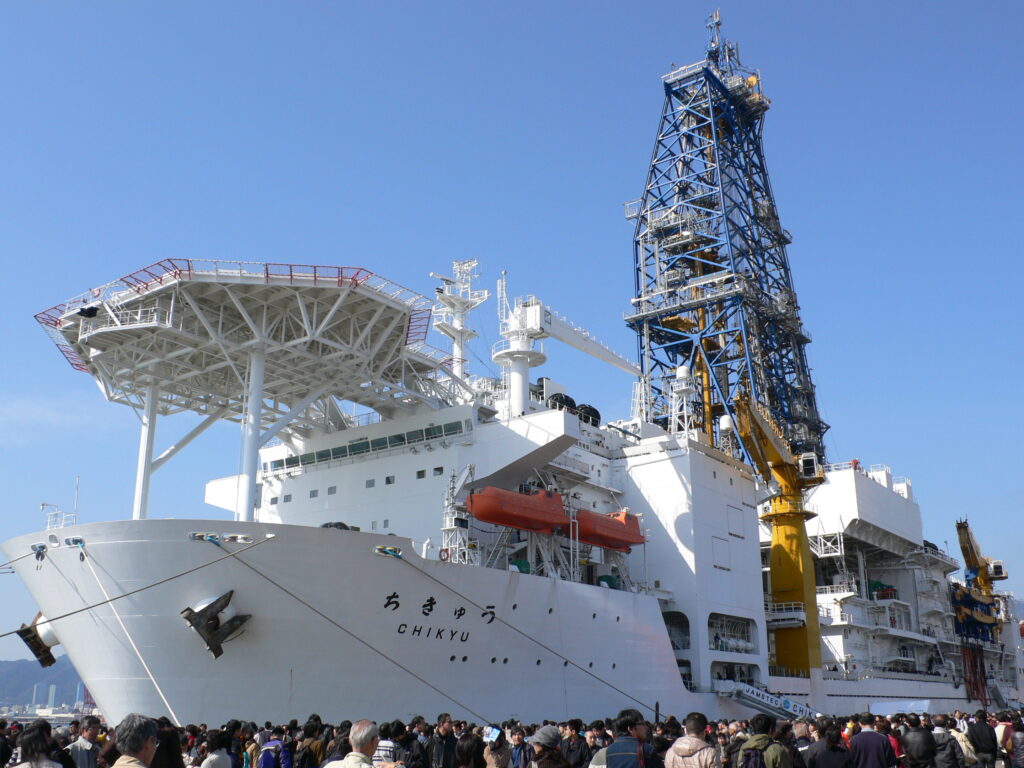
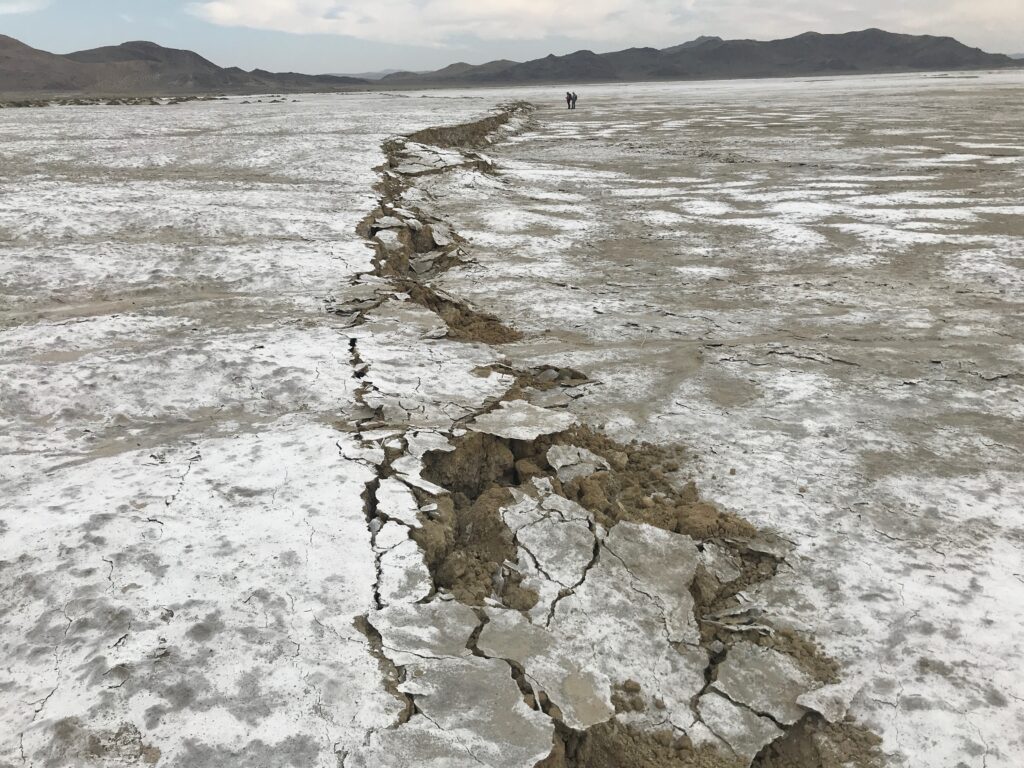
Scientists who drilled deeper into an undersea earthquake fault than ever before have found that the tectonic stress in Japan’s Nankai subduction zone is less than expected, according to a study from researchers at The University of Texas at Austin and University of Washington. The findings, published in the journal Geology, are a puzzle because… Continue Reading Deepest Scientific Ocean Drilling Sheds Light on Japan’s Next Great Earthquake
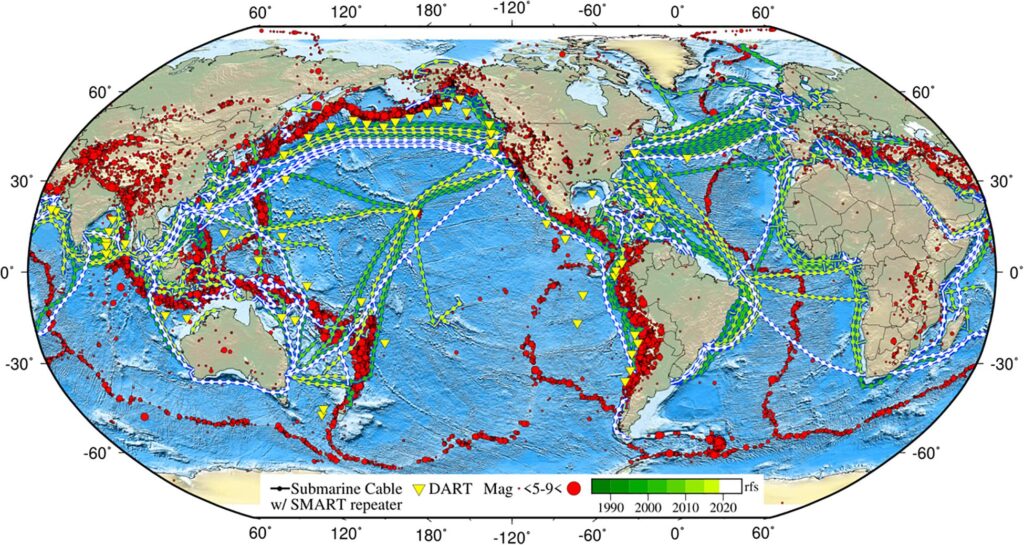
Century-Old Technology Inspires Method for Early Warning Tsunami and Earthquake Detection
A million kilometers of fiber optic cable lie on the ocean floor, carrying telecommunication signals across vast stretches of ocean to keep the whole world connected. A new international collaboration, including experts from The University of Texas at Austin, aims to turn them into a global early warning system for tsunamis and earthquakes, as well… Continue Reading Century-Old Technology Inspires Method for Early Warning Tsunami and Earthquake Detection
Big Data Imaging Shows Rock’s Big Role in Channeling Earthquakes in Japan
Thanks to 20 years of seismic data processed through one of the world’s most powerful supercomputers, scientists have created the first complete, 3D visualization of a mountain-size rock called the Kumano Pluton buried miles beneath the coast of southern Japan. They can now see the rock could be acting like a lightning rod for the… Continue Reading Big Data Imaging Shows Rock’s Big Role in Channeling Earthquakes in Japan
Are Deep Fluids Behind the Largest Earthquakes? ‘Not So Fast!’ Says UT Graduate Student
Sandwiched between tectonic plates are layers of material that show up as thin shadows on seismic tomography, a kind of CT scan of the Earth. For years, scientists assumed the anomalies were signs of highly pressurized water squeezed into densely packed rock and that the fluid acted as a kind of hair-trigger on earthquake faults.… Continue Reading Are Deep Fluids Behind the Largest Earthquakes? ‘Not So Fast!’ Says UT Graduate Student
Seismic Shockwave Pattern May Be Redirecting Earthquake Damage
New research from The University of Texas at Austin could change the way scientists think about potential damage from earthquakes. The study examined data from one of the densest seismic arrays ever deployed and found that earthquakes emit their strongest seismic shockwaves in four opposing directions. The effect, which leaves a pattern resembling a four-leaf… Continue Reading Seismic Shockwave Pattern May Be Redirecting Earthquake Damage