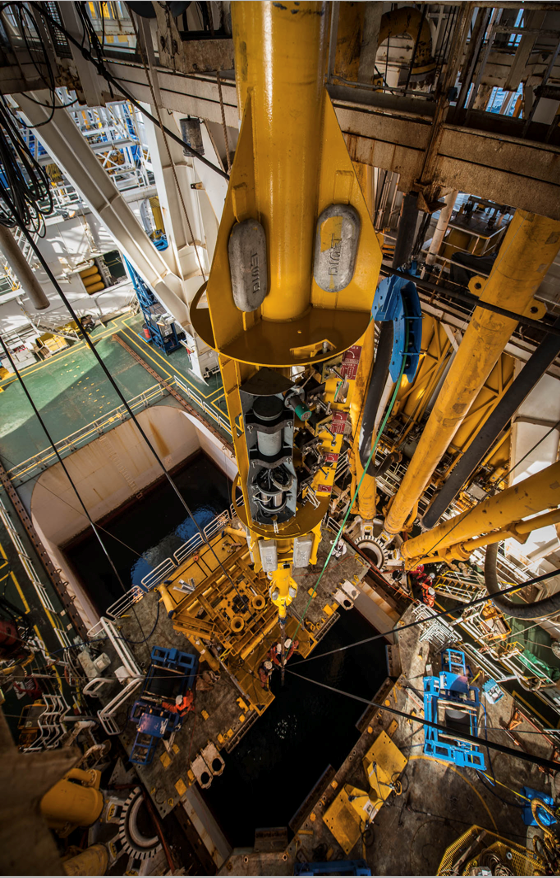
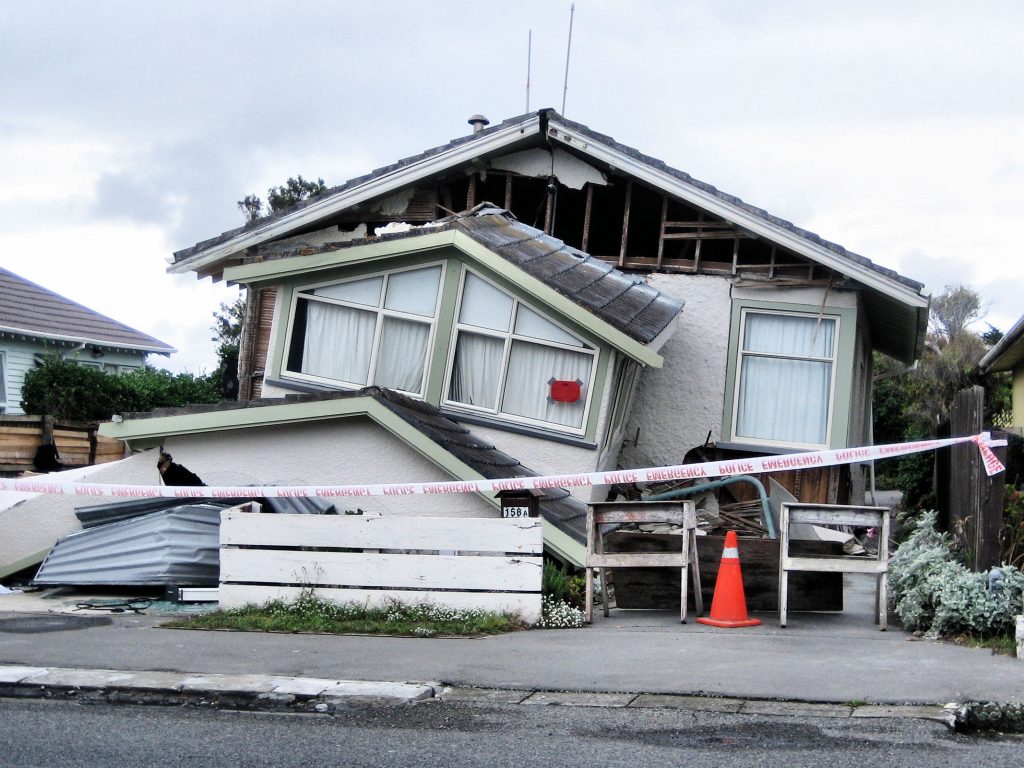
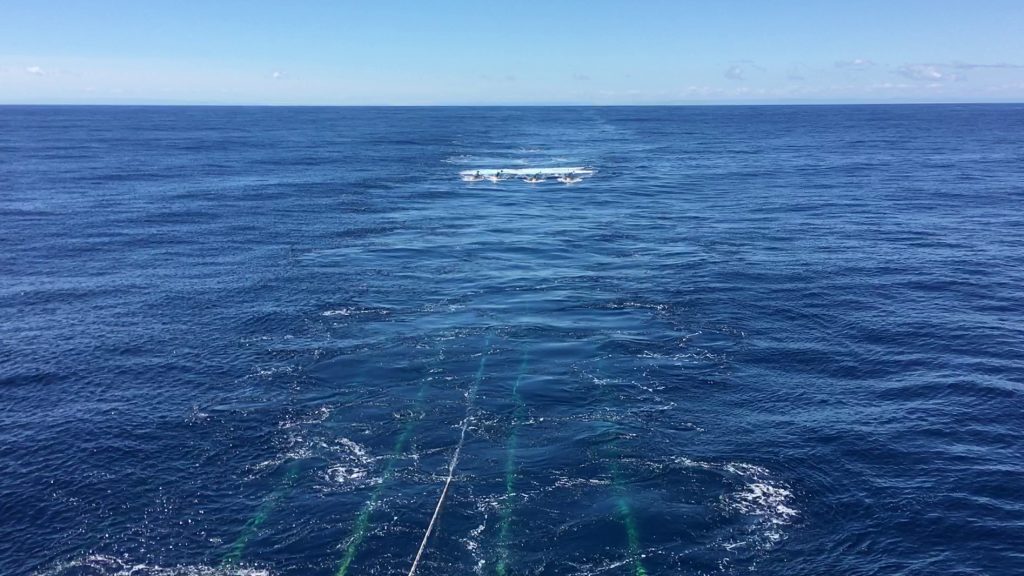
Scientists for the first time have detected a slow slip earthquake in motion during the act of releasing tectonic pressure on a major fault zone at the bottom of the ocean. The slow earthquake was recorded spreading along the tsunami-generating portion of the fault off the coast of Japan, behaving like a tectonic shock absorber.… Continue Reading Scientists Capture Slow-Motion Earthquake in Action
Articles about earthquake research and scientists at the University of Texas Institute for Geophysics. For more information contact costa@ig.utexas.edu
Scientists Isolate Early-Warning Tremor Pattern in Lab-Made Earthquakes
Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have successfully isolated a pattern of lab-made ‘foreshock’ tremors. The finding offers hope that future earthquakes could be forecast by the swarm of smaller tremors that come before them. The research was published in the journal Nature Communications. The next step is to replicate the results in… Continue Reading Scientists Isolate Early-Warning Tremor Pattern in Lab-Made Earthquakes
Discovery of Massive Undersea Water Reservoir Could Explain New Zealand’s Mysterious Slow Earthquakes
Researchers have discovered a sea’s worth of water locked within the sediment and rock of a lost volcanic plateau that’s now deep in the Earth’s crust. Revealed by a 3D seismic image, the water lies two miles under the ocean floor off the coast of New Zealand, where it may be dampening a major earthquake… Continue Reading Discovery of Massive Undersea Water Reservoir Could Explain New Zealand’s Mysterious Slow Earthquakes
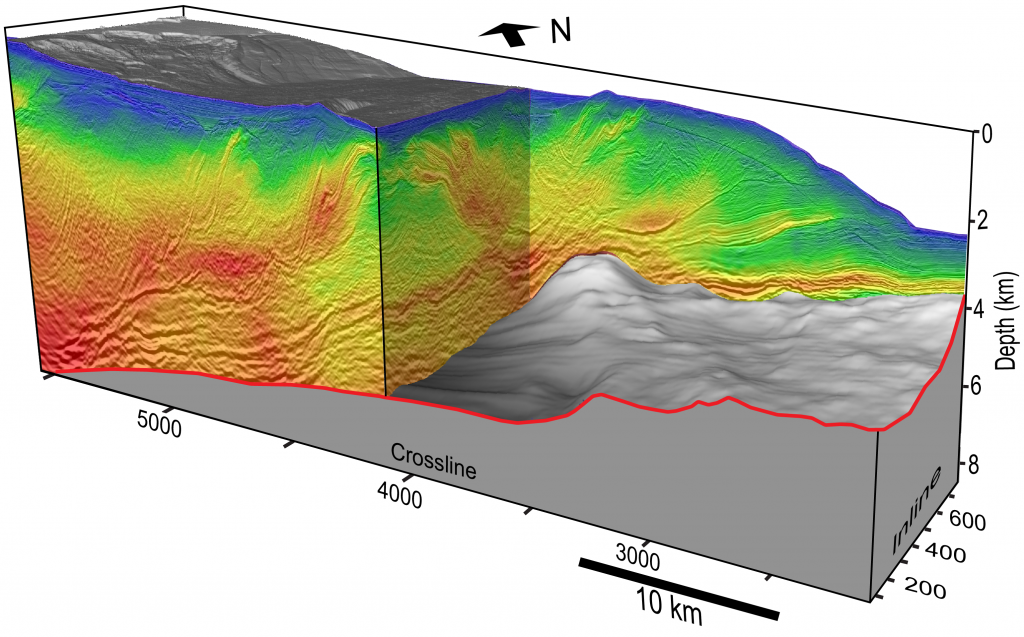
Sinking Seamount Offers Clues to Slow Motion Earthquakes
Scientists have long puzzled over what happens when seamounts — mountains and volcanoes on the seafloor — are pulled into subduction zones. Now, new research from The University of Texas at Austin shows that when seamounts sink, they leave behind a trail of soft sediments. The researchers think the sediment patches help tectonic pressure escape… Continue Reading Sinking Seamount Offers Clues to Slow Motion Earthquakes
Earthquake Scientists Have a New Tool in the Race to Find the Next Big One
An everyday quirk of physics could be an important missing piece in scientists’ efforts to predict the world’s most powerful earthquakes. In a study published in the journal Science, researchers at The University of Texas at Austin discovered that a frictional phenomenon could be key to understanding when and how violently faults move. That’s because… Continue Reading Earthquake Scientists Have a New Tool in the Race to Find the Next Big One
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 7
- Next Page »