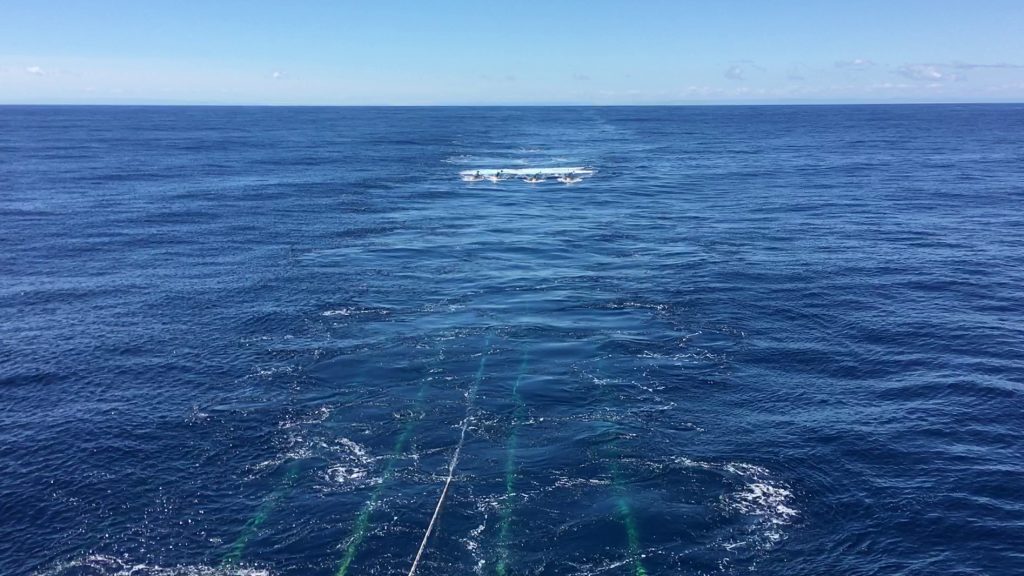
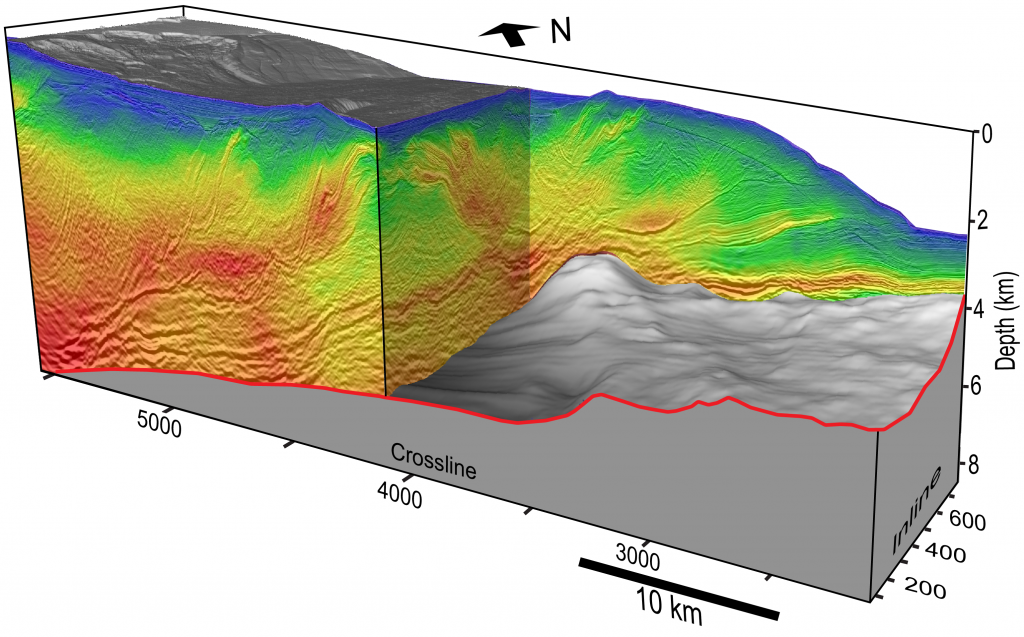
Researchers have discovered a sea’s worth of water locked within the sediment and rock of a lost volcanic plateau that’s now deep in the Earth’s crust. Revealed by a 3D seismic image, the water lies two miles under the ocean floor off the coast of New Zealand, where it may be dampening a major earthquake… Continue Reading Discovery of Massive Undersea Water Reservoir Could Explain New Zealand’s Mysterious Slow Earthquakes
Sinking Seamount Offers Clues to Slow Motion Earthquakes
Scientists have long puzzled over what happens when seamounts — mountains and volcanoes on the seafloor — are pulled into subduction zones. Now, new research from The University of Texas at Austin shows that when seamounts sink, they leave behind a trail of soft sediments. The researchers think the sediment patches help tectonic pressure escape… Continue Reading Sinking Seamount Offers Clues to Slow Motion Earthquakes
In Search of the Next Big One
Subduction zones are the source of the world’s most dangerous earthquakes and tsunamis. UTIG’s researchers are on a mission to understand them By Constantino Panagopulos On Jan. 26, 1700, a barrage of tsunamis ripped across the Pacific Ocean at the speed of a jet liner. The 100-foot waves slammed into the northwest coast of America… Continue Reading In Search of the Next Big One